In the tapestry of human aesthetics, hair occupies a prominent place, particularly for men. It’s a symbol of virility, confidence, and youth. Yet, the unfortunate reality is that hair loss, a common affliction among men, can shatter this delicate balance, leaving many feeling distressed and insecure.
This comprehensive guide delves into the intricate world of hair loss in men, exploring the underlying causes that trigger this distressing condition. From genetic predispositions to lifestyle choices, we’ll unravel the mysteries behind thinning locks and empower men with knowledge to combat this prevalent issue.
Causes of Hair Loss in Men
Hair loss, also known as alopecia, is a common condition that affects millions of men worldwide. It can be a source of distress and embarrassment, and it can significantly impact a man’s self-confidence. While there are many factors that can contribute to hair loss, some of the most common causes include genetics, hormones, aging, and certain medical conditions.
This article explores the various causes of hair loss in men, providing insights into the underlying mechanisms and potential treatments. By understanding the root causes of hair loss, men can take proactive steps to prevent or manage this condition.
Genetics
Genetics plays a significant role in hair loss. Certain genes are associated with an increased risk of male pattern baldness, also known as androgenetic alopecia. This condition is characterized by a receding hairline and thinning hair on the crown of the head.
The genes responsible for male pattern baldness are passed down from both parents, and they determine the sensitivity of hair follicles to a hormone called dihydrotestosterone (DHT).
DHT is a derivative of testosterone, and it is responsible for the development of male secondary sexual characteristics, such as facial hair and a deep voice. However, DHT can also bind to receptors on hair follicles, causing them to shrink and eventually stop producing hair.
Hormones
Hormonal changes can also contribute to hair loss in men. Androgens, such as testosterone and DHT, are the primary hormones involved in male hair growth. However, an imbalance of these hormones, or a sensitivity to them, can lead to hair loss.
For example, high levels of DHT can cause hair follicles to shrink and produce thinner, weaker hair. Additionally, a condition called hyperthyroidism, which is an overactive thyroid gland, can also lead to hair loss.
Aging
As men age, they experience a gradual decline in testosterone production. This can lead to a decrease in hair growth and an increase in hair loss. Additionally, the hair follicles themselves become weaker and more susceptible to damage as men age.
This age-related hair loss is a natural process, and it is not typically a cause for concern. However, some men may experience more significant hair loss than others, and they may benefit from medical intervention.
Medical Conditions
Certain medical conditions can also cause hair loss in men. These conditions include:
- Alopecia areata: This is an autoimmune condition that causes hair loss in patches.
- Lupus: This is a chronic autoimmune disease that can affect the skin, joints, and other organs, including the hair follicles.
- Cancer: Some types of cancer, such as chemotherapy, can cause hair loss.
- Medications: Certain medications, such as chemotherapy drugs and blood thinners, can cause hair loss as a side effect.
Male Pattern Baldness (Androgenetic Alopecia)

Male pattern baldness, also known as androgenetic alopecia, is the most common cause of hair loss in men. It is a genetic condition that is triggered by the male hormone testosterone.
Testosterone is converted into dihydrotestosterone (DHT) by an enzyme called 5-alpha-reductase. DHT binds to receptors on the hair follicles, causing them to shrink and eventually stop producing hair. This process is called miniaturization.
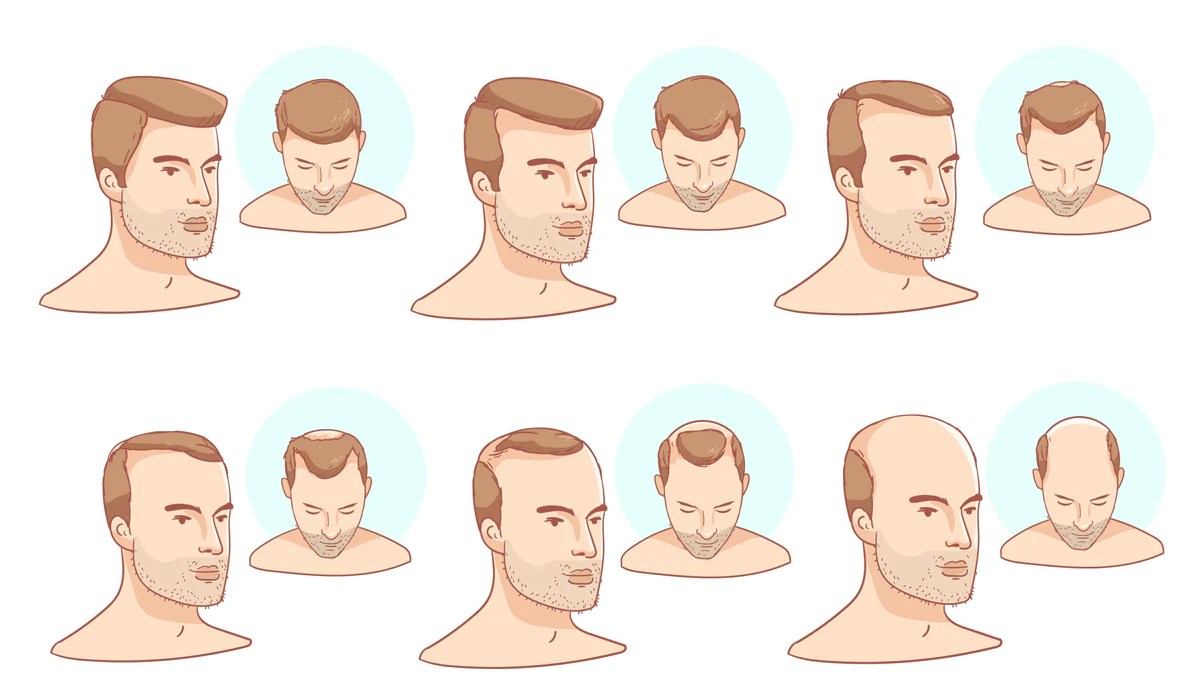
Stages of Male Pattern Baldness
Male pattern baldness typically progresses through several stages:
- Stage 1: Slight thinning of hair at the temples and crown.
- Stage 2: Continued thinning of hair at the temples and crown, with some hair loss at the front of the scalp.
- Stage 3: Significant hair loss at the temples and crown, with a receding hairline.
- Stage 4: Further hair loss at the temples and crown, with a bald spot forming at the top of the scalp.
- Stage 5: Complete baldness at the top of the scalp, with only a horseshoe-shaped ring of hair remaining around the sides and back of the head.
Hormonal Factors
Hormonal fluctuations play a significant role in hair loss, particularly in men. The primary hormone involved in male pattern baldness is dihydrotestosterone (DHT), a derivative of testosterone. DHT binds to receptors in hair follicles, causing them to miniaturize and eventually stop producing hair.
The Role of Dihydrotestosterone (DHT)
DHT is a potent androgen that is converted from testosterone by the enzyme 5-alpha-reductase. It is responsible for the development of male secondary sexual characteristics, such as facial hair and a deep voice. DHT also plays a role in hair growth, but in some men, it can cause hair follicles to shrink and produce thinner, weaker hair until eventually, they stop producing hair altogether.
Hormonal Changes with Age
As men age, their testosterone levels gradually decline, while DHT levels may remain relatively stable or even increase. This hormonal shift can lead to an increased risk of hair loss. Additionally, the aging process itself can cause changes in hair follicles, making them more susceptible to the effects of DHT.
The Link Between Testosterone and Hair Loss
While testosterone is essential for male sexual development and function, it can also contribute to hair loss. High levels of testosterone can be converted to DHT, which, as discussed earlier, can lead to hair follicle miniaturization and hair loss. However, it is important to note that not all men with high testosterone levels experience hair loss.
Genetic factors and other individual characteristics also play a role.
Medical Conditions and Treatments
Certain medical conditions and treatments can also contribute to hair loss in men. Understanding the underlying causes is essential for addressing and managing hair loss effectively.
Medical Conditions
Various medical conditions can lead to hair loss in men, including:
- Alopecia Areata: An autoimmune condition that causes hair loss in patches.
- Thyroid Disorders: Both hyperthyroidism (overactive thyroid) and hypothyroidism (underactive thyroid) can cause hair loss.
- Lupus: An autoimmune disease that can affect the skin, joints, and organs, including the hair follicles.
- Cancer: Certain types of cancer and their treatments, such as chemotherapy and radiation therapy, can cause hair loss.
- Ringworm: A fungal infection of the scalp that can lead to hair loss.
- Trichotillomania: A mental health condition that involves recurrent, irresistible urges to pull out hair from the scalp, eyebrows, or other body areas.
Medications and Treatments
Some medications and treatments can also cause hair loss as a side effect. These include:
- Chemotherapy and Radiation Therapy: These cancer treatments can damage hair follicles, leading to temporary or permanent hair loss.
- Blood Thinners: Certain blood thinners, such as warfarin and heparin, can cause hair loss as a rare side effect.
- Antidepressants: Some antidepressants, such as tricyclic antidepressants and selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), can cause hair loss as a side effect.
- Anticonvulsants: Certain anticonvulsants, such as valproic acid and phenytoin, can cause hair loss as a side effect.
- Hormone Replacement Therapy: Hormone replacement therapy for conditions like prostate cancer or transgender transition can sometimes cause hair loss as a side effect.
- Anabolic Steroids: Anabolic steroids, often used for muscle building, can cause hair loss as a side effect.
Lifestyle Factors

Lifestyle choices can significantly impact hair loss in men. Stress, diet, and smoking are some of the key factors that can contribute to hair loss or exacerbate existing conditions.
Stress
Chronic stress can trigger hair loss by disrupting the normal hair growth cycle. When under stress, the body releases hormones like cortisol, which can lead to inflammation and damage to hair follicles. This can result in increased hair shedding and difficulty in hair growth.
Diet
A healthy diet rich in vitamins, minerals, and proteins is essential for healthy hair growth. Deficiencies in certain nutrients, such as iron, zinc, biotin, and protein, can lead to hair loss. Eating a balanced diet that includes plenty of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins can help promote healthy hair growth.
Smoking
Smoking is a major risk factor for hair loss. The chemicals in cigarettes can damage blood vessels, restrict blood flow to the scalp, and hinder the delivery of nutrients to hair follicles. This can lead to hair loss and premature graying.
Lifestyle Modifications for Hair Health
- Managing Stress: Techniques like meditation, yoga, and exercise can help manage stress levels and reduce the risk of stress-induced hair loss.
- Healthy Diet: Eating a balanced diet rich in essential nutrients is crucial for healthy hair growth. Including foods high in iron, zinc, biotin, and protein can promote thicker, healthier hair.
- Quitting Smoking: Smoking cessation is one of the most effective ways to prevent or slow down hair loss caused by smoking. Quitting smoking can improve overall health and well-being, including hair health.
Nutritional Deficiencies
Nutritional deficiencies can play a significant role in hair loss among men. Hair growth and health rely on a balanced intake of vitamins, minerals, and other essential nutrients. Deficiencies in certain nutrients can disrupt hair growth cycles, leading to thinning hair or even baldness.
Vitamins and Minerals for Hair Health
Several vitamins and minerals are crucial for maintaining healthy hair growth. These include:
- Vitamin A: Supports the production of sebum, a natural oil that keeps hair moisturized and prevents dryness.
- B Vitamins (especially Biotin): Essential for cell growth and metabolism, including hair growth.
- Vitamin C: Aids in the absorption of iron, which is important for hair growth.
- Vitamin D: Plays a role in hair follicle cycling and may be linked to hair loss when deficient.
- Iron: Carries oxygen to hair follicles, promoting healthy hair growth. Iron deficiency can lead to hair loss.
- Zinc: Involved in hair protein synthesis and cell division, contributing to healthy hair growth.
Dietary Changes for Hair Health
Incorporating a balanced diet rich in essential nutrients can help promote healthy hair growth and prevent deficiencies that may contribute to hair loss. Some dietary changes that may benefit hair health include:
- Consuming a variety of fruits and vegetables: Provides a wide range of vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants that support hair health.
- Including lean protein sources: Protein is essential for hair growth, so incorporating lean meats, poultry, fish, and plant-based proteins is beneficial.
- Eating whole grains: Whole grains provide essential vitamins, minerals, and fiber, which contribute to overall health and may benefit hair growth.
- Limiting processed foods and sugary drinks: These foods offer little nutritional value and may contribute to inflammation, which can negatively impact hair health.
- Staying hydrated: Drinking plenty of water is essential for overall health and can also benefit hair health by keeping hair follicles hydrated and promoting healthy hair growth.
Hair Care Practices

Hair care practices play a crucial role in maintaining hair health and preventing hair loss. Certain habits and treatments can damage hair follicles, leading to thinning and breakage. Understanding the impact of hair care practices on hair health is essential for adopting a gentle and protective approach to hair care.
Harsh Chemicals
Exposure to harsh chemicals, such as those found in some hair dyes, bleaching agents, and styling products, can damage the hair shaft and scalp. These chemicals can strip away natural oils, causing hair to become dry, brittle, and more prone to breakage.
Additionally, some chemicals, such as formaldehyde, have been linked to an increased risk of hair loss.
Heat Styling Tools
Excessive use of heat styling tools, such as blow dryers, flat irons, and curling irons, can also contribute to hair loss. High temperatures can damage the hair shaft, causing it to become weak and brittle. Additionally, heat styling tools can strip away natural oils, leading to dryness and breakage.
Tight Hairstyles
Tight hairstyles, such as cornrows, braids, and ponytails, can put excessive tension on the hair follicles, leading to traction alopecia. This type of hair loss occurs when the hair follicles are repeatedly pulled or stretched, causing them to become damaged and eventually stop producing hair.
Gentle Hair Care Practices
Adopting gentle hair care practices can help prevent hair loss and maintain hair health. Some key practices include:
- Use mild shampoos and conditioners that are free of harsh chemicals.
- Avoid excessive washing, as this can strip away natural oils.
- Use a wide-toothed comb to detangle hair gently, starting from the ends and working your way up.
- Avoid brushing hair when wet, as it is more prone to breakage.
- Limit the use of heat styling tools and use them at a low temperature setting.
- Avoid tight hairstyles that put tension on the hair follicles.
- Protect hair from sun exposure by wearing a hat or scarf.
- Maintain a healthy diet that includes plenty of fruits, vegetables, and whole grains.
By following these gentle hair care practices, you can help maintain hair health and reduce the risk of hair loss.
Psychological Impact of Hair Loss

Hair loss in men can have a significant impact on their emotional and psychological well-being. Losing hair can be a traumatic experience that affects self-esteem, confidence, and social interactions.The psychological impact of hair loss can vary from mild to severe.
Some men may experience feelings of embarrassment, shame, and anxiety. They may feel less attractive and less confident in their appearance. Hair loss can also lead to social isolation and withdrawal from activities that they once enjoyed.
Coping Mechanisms and Support Groups
There are several coping mechanisms that men can use to deal with the psychological impact of hair loss. These include:
- Accepting the Reality: Coming to terms with hair loss and accepting it as a natural part of life can help reduce feelings of distress and anxiety.
- Focusing on Strengths: Shifting the focus from hair loss to other positive aspects of one’s appearance and personality can boost self-esteem and confidence.
- Seeking Professional Help: Consulting with a therapist or counselor can provide emotional support and guidance in developing coping strategies.
- Joining Support Groups: Connecting with other men who are experiencing hair loss can offer a sense of community and shared experiences.
Support groups can be a valuable resource for men experiencing hair loss. These groups provide a safe space for men to share their experiences, offer support to one another, and learn about coping mechanisms.
Conclusion
Hair loss in men is a common issue that can have various causes, ranging from genetic factors to lifestyle habits. Understanding the underlying causes of hair loss is crucial for effective prevention and treatment. Early detection and intervention can help manage hair loss and preserve hair follicles.
Consulting a healthcare professional, such as a dermatologist or trichologist, is highly recommended to determine the specific cause of hair loss and receive personalized advice and treatment options. Seeking professional guidance can help individuals address their hair loss concerns effectively and improve their overall hair health.
Last Word

In conclusion, hair loss in men is a complex phenomenon influenced by a myriad of factors. Understanding the underlying causes is crucial for developing effective prevention and treatment strategies. Early detection and intervention are paramount, as timely action can mitigate the severity of hair loss and restore confidence.
For personalized guidance and tailored treatment options, consulting a healthcare professional is highly recommended. They can assess individual circumstances, provide accurate diagnoses, and prescribe appropriate medications or therapies to address the specific cause of hair loss.
Q&A
Can stress contribute to hair loss in men?
While stress alone may not directly cause hair loss, it can exacerbate existing conditions or trigger temporary hair shedding. Managing stress levels through relaxation techniques, exercise, or seeking professional help can be beneficial.
Does diet play a role in hair loss?
A balanced diet rich in essential vitamins, minerals, and proteins is crucial for overall hair health. Deficiencies in certain nutrients, such as iron, zinc, or biotin, can contribute to hair loss. Maintaining a healthy diet supports healthy hair growth.
How do hair care practices impact hair loss?
Harsh chemicals, excessive heat styling, and tight hairstyles can damage hair and contribute to breakage. Opting for gentle hair care products, using heat protectants, and avoiding tight hairstyles can help preserve hair health and prevent unnecessary hair loss.



